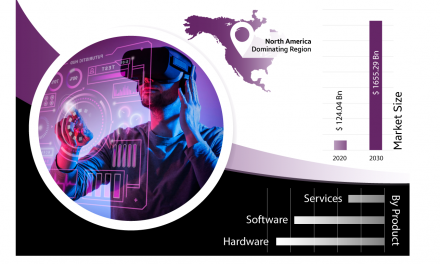
The concept of the Metaverse has captured the imagination of technology enthusiasts and visionaries alike. With the increasing expenditure on digital solutions and cutting-edge technologies, the Metaverse is poised to become a transformative force in the digital landscape. According to a recent report by Allied Market Research1, the Metaverse market is projected to reach a staggering worth of $993.86 billion by 2030. This article explores the potential of the Metaverse, its impact on various industries, and the driving factors behind its exponential growth.
Understanding the Metaverse
Defining the Metaverse
The Metaverse refers to a virtual reality space where users can interact with a computer-generated environment and other participants in real-time. It goes beyond traditional virtual reality experiences by creating immersive, interconnected digital worlds that transcend individual platforms or applications. The Metaverse aims to blend the virtual and physical realms seamlessly, providing users with a sense of presence and social interaction.
Key Elements and Features
The Metaverse is characterized by several key elements and features:
- Virtual Environments: The Metaverse comprises diverse virtual environments, ranging from realistic simulations of the physical world to fantastical realms limited only by imagination. These environments are designed to be interactive, visually engaging, and capable of supporting a variety of activities and experiences.
- User Interactivity: In the Metaverse, users can actively participate and shape their digital experiences. They can create, modify, and explore virtual content, collaborate with others, and engage in social interactions through avatars or digital representations of themselves.
- Cross-Platform Connectivity: One of the fundamental aspects of the Metaverse is its ability to connect users across different platforms, devices, and applications. This interoperability allows for seamless transition and continuity of experiences, enabling users to move fluidly between various virtual worlds and services.
- Economy and Commerce: The Metaverse is expected to have a thriving digital economy, where users can engage in virtual transactions, own and trade digital assets, and participate in virtual marketplaces. This economic aspect opens up new opportunities for businesses, creators, and entrepreneurs within the Metaverse ecosystem.
The Growth Potential of the Metaverse
Market Size and Projection
The Allied Market Research report projects the Metaverse market to be worth $993.86 billion by 2030, driven by increasing expenditure on digital solutions and cutting-edge technologies1. Several factors contribute to this exponential growth:
Technological Advancements: Advancements in virtual reality, augmented reality, artificial intelligence, and blockchain technologies are laying the foundation for the Metaverse’s development. These technologies enable more immersive experiences, realistic graphics, intelligent virtual entities, and secure decentralized systems, enhancing the overall user experience.
Changing Consumer Behavior: The pandemic has accelerated the shift towards digital engagement, remote work, and virtual social interactions. As individuals seek new ways to connect, entertain, and conduct business in the digital realm, the Metaverse offers a compelling solution by providing immersive and collaborative experiences.
Industry Applications: The potential applications of the Metaverse span across various industries, including gaming, entertainment, education, healthcare, retail, and real estate. From virtual conferences and concerts to virtual training simulations and digital marketplaces, the Metaverse presents new avenues for innovation, efficiency, and monetization.
Challenges and Considerations
While the Metaverse holds tremendous potential, it also faces several challenges that need to be addressed:
- Technical Infrastructure: Building the Metaverse requires robust technical infrastructure capable of supporting massive user bases, high-performance computing, low-latency networks, and secure data storage. The development and scalability of these infrastructure components pose significant challenges.
- Interoperability and Standards: Achieving seamless interoperability between different platforms, applications, and devices is crucial for the success of the Metaverse. Establishing industry-wide standards and protocols will be essential to enable smooth transitions and experiences across the digital landscape.
- Privacy and Security: As the Metaverse collects and processes vast amounts of user data, ensuring privacy and security becomes paramount. Safeguarding personal information, preventing data breaches, and addressing cybersecurity risks are critical considerations that must be addressed to build trust within the Metaverse ecosystem.
Embracing the Metaverse: Opportunities and Implications
Opportunities for Businesses and Entrepreneurs
The Metaverse presents a plethora of opportunities for businesses and entrepreneurs to innovate and thrive:
- New Revenue Streams: Within the Metaverse, businesses can explore new revenue streams through virtual product offerings, in-game purchases, virtual real estate development, and digital advertising. These avenues allow for monetization and engagement with a global audience.
- Enhanced Customer Experiences: By leveraging the immersive nature of the Metaverse, businesses can create unique and captivating customer experiences. Virtual showrooms, interactive simulations, and personalized interactions offer novel ways to engage and delight customers.
- Collaborative Environments: The Metaverse fosters collaboration and co-creation. Businesses can leverage these capabilities to facilitate remote teamwork, virtual meetings, and innovative problem-solving, transcending geographical boundaries and time zones.
Societal and Cultural Implications
The widespread adoption of the Metaverse will have significant societal and cultural implications:
- Digital Inclusion: The Metaverse has the potential to bridge geographical and socioeconomic gaps, providing access to virtual experiences, education, and opportunities for individuals who might otherwise be marginalized. Ensuring equitable access and inclusion will be crucial for a fair and diverse Metaverse.
- Reimagining Social Interactions: The Metaverse introduces new possibilities for social interactions, allowing individuals to connect, socialize, and build communities in virtual spaces. This transformation may reshape traditional notions of communication, relationships, and identity.
- Ethical Considerations: As the Metaverse blurs the boundaries between reality and the digital realm, ethical considerations surrounding data privacy, content moderation, virtual identity, and algorithmic bias come to the forefront. Robust ethical frameworks and responsible governance will be essential to navigate these challenges.
Conclusion
The Metaverse represents a paradigm shift in the digital landscape, offering immersive and interconnected virtual experiences. With a projected market size of $993.86 billion by 2030, the Metaverse holds tremendous potential across various industries. However, addressing technical, interoperability, and security challenges will be crucial to realizing this potential. Embracing the opportunities presented by the Metaverse can lead to enhanced customer experiences, new revenue streams, and societal transformations. As the Metaverse continues to evolve, it is imperative for stakeholders to collaborate, establish standards, and foster responsible innovation to create a vibrant, inclusive, and sustainable digital future.
Source: Allied Market Research. “Metaverse Market Size Worth $993.86 Billion by 2030: Increasing Expenditure on Digital Solutions & Cutting-Edge Technologies.” GlobeNewswire. June 7, 2023. (link)